1.4.3 How to Read an Activity Diagram
A UML Activity Diagram represents the actions/logic of a single method in code.
Below is an example of a block of code and the corresponding Activity Diagram.
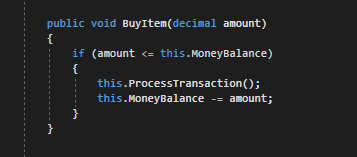
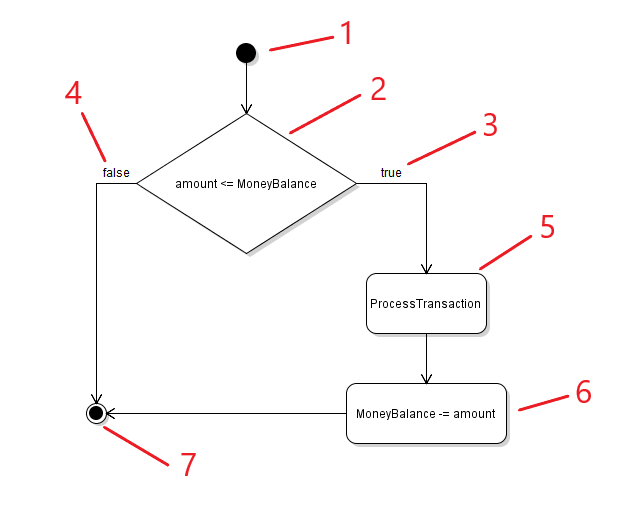
- The Scenario start node. Also the opening curly brace of a method.
- The Decision to be made. Also called the conditional statement.
- The line that represents if the conditional statement evaluates to true.
- The line that represents if the conditional statement evaluates to false.
- An Activity taking place. In this example, the activity is a method call that may have its own set of logic checks.
- An Activity taking place. In this example, this is a line of code that subtracts the amount from the MoneyBalance.
- The Scenario end node. Also the closing curly brace of a method.
As the code inside the BuyItem method executes, if the amount parameter is less than or equal to the current instance's MoneyBalance, the conditional statement will evaluate to true and both the ProcessTransaction method and the MoneyBalance will be reduced by the amount.
However, if the amount parameter is greater than the current instance's MoneyBalance, nothing will happen and the method will end.

