Separating ideas from instances of those ideas. Something abstract is generic and is not a concrete or physical thing.
A process taking place.
A value or reference being passed into a method call.
Giving a value to a variable or field - i.e. foo = 5;
A relationship between classes.
A window in the debugger that shows information it guesses to be relevant.
A debugging tool that stops an application in a specific place when it is run.
True or false. Used for evaluating yes/no questions. Ex. true, false
A general purpose and object-oriented programming language.
A window in the debugger that shows the levels of method calls, with the lowest level being the first call and the highest level being the current spot in the application.
"Transforming" or "morphing" an object into a different type. Objects can be cast into more generic or more specialized types.
A template for creating objects. A class is to an object as a blueprint is to a house.
An issue in code that prevents an application from properly building and running.
An issue in code that will not prevent an application from properly building, but may indicate other possible errors.
To process of going through code to identify and solve an issue.
A fractional number ending with "m". Used for both large and precise numbers such as money balances. Ex 5.25m
A conditional statement.
Creating a field or variable with no value - i.e. public int Foo;
A fractional number with an optional decimal point. Used for measuring things such as height, width, weight, temperature. Ex. 5.25
The idea of hiding information.
An event that occurs during runtime that disrupts the regular flow of an application.
The automated system used to process student assignments.
Attributes that define a class.
F12. Locates where a certain "thing" is defined in code.
Basing one object/class on another. Similar to the classification of animals.
An instance is a singular occurrence of a thing. In code, the keyword 'new' instantiates new instances of classes. The instance is unrelated to anything else. This is much like how when you open up a new window of a browser or file explorer, that is a new instance of that program.
Create an instance of a class - i.e. new Bar();
A whole number. Used for counting things such as quantity. Ex. 5
Made up of methods and properties that do not declare any implementation. Classes that implement an interface must implement all members of that interface.
A window in the debugger that shows information present in the file the application is currently located in.
Any "thing" within a class. This includes fields, methods, constructors, properties, etc.
Used when a particular object needs to "do something". Controls the main flow of the application.
Makes code "do stuff". Defines the behaviors of a class.
A word that a something is referred to as.
The value of an object when its value has not been assigned yet.
Does not have a reference. If an object without another reference to is is assigned null the object will no longer be in memory. If the an object has another reference to it, the reference to the object no longer exists, but the object will still exist.
Used in sequence diagrams. Signifies an object is going to either make a call or be called on.
When an object is assigned to a field or variable.
An instance of a class. An object is to a class as a house is to a blueprint.
Modeling the world in objects, which group data and behavior together.
Information that a method needs in order to properly function, usually passed in as an argument in a method call.
Passing an object reference into a method call gives that parameter access to all of the visible members of that particular object.
Passing a value into a method call assigns the matching parameter to that value.
The idea that a single object can be used in different ways, and different objects can be used the same way.
Allows other classes/objects to have to ability to read or change the private values of a class/object.
Exits the current method and goes back to where it was called with a value or reference.
The code region in which a variable or field can be referred to.
F11. Makes the debugger move into the next line of code in the sequence, going into any of its details.
F10. Makes the debugger execute a line of code without going into any of its details.
Alphanumeric or text data. Used for things such as name, address, description. Ex. "Foo"
A comestic issue that doesn't follow the rules of the style guide.
An analyzer package used to help follow style rules when writing code.
The current instance of the current class.
Indicates how a field/variable/etc. is intended to be used.
Represents the actions/logic of a single method in code.
Represents an application's structure. Is the "blueprint" of an application.
Represents a particular point in time when an application is running.
Represents the flow of method calls and returns in an application.
Unified Modeling Language. A standardized way of modeling software systems.
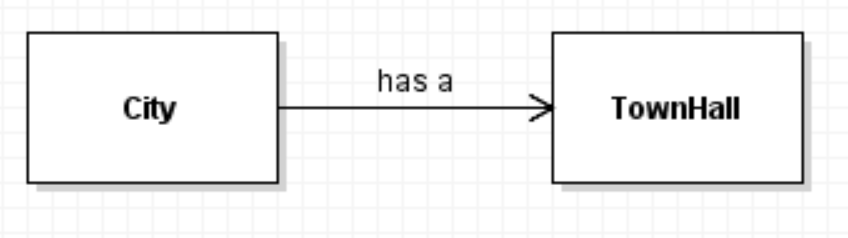
Is associated with defines a "has a" relationship between classes. A city has a TownHall.
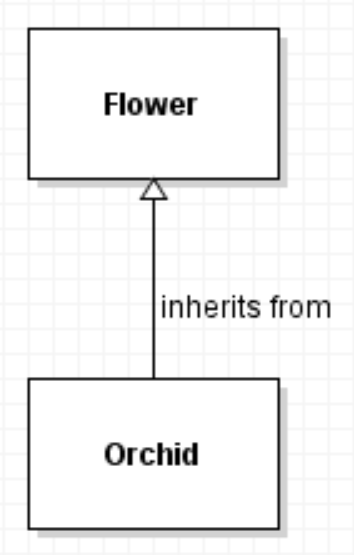
Inherits from indicates one class inherits from another. Orchid inherits from Flower.
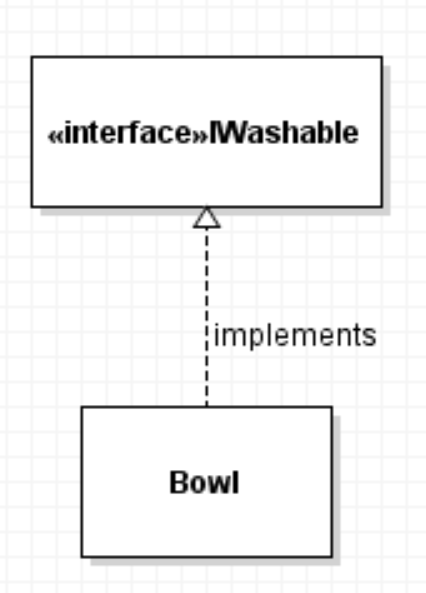
Implements interface indicates a class implements an interface. Bowl implements IWashable.
Is composed of indicates a class is compsosed of another. Face is composed of Nose.

A local value/reference that only exists in the scope of its definition.
A program used to make UML diagrams.
The level of access for a particular class/field/method/etc.
An IDE (integrated development environment) that allows the writing and editing of code.