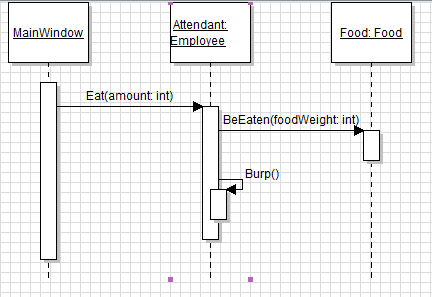
Let's say we have an employee that is eating some food, but there is no way to ensure that the food is actually eaten; the weight of the food never goes down. So we'd like to make it so that the food weight is decreased when the employee eats.
Currently we are working with an Eat method that looks like this:
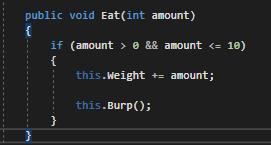
Because we have the amount parameter that references the Food item's weight, we can use it however we want.
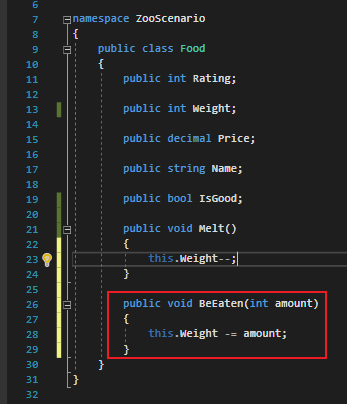
So let's define a method in the Food class called BeEaten that has a parameter named amount of type int and reduces the Food item's Weight by the amount parameter.
We can now call BeEaten from the the Eat method on the Employee's Food object and pass in the amount parameter already in the method.
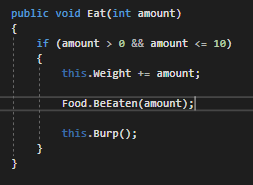
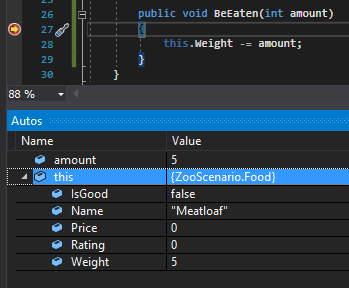
If we run the application we can see that the amount parameter in the BeEaten method has a value of 5, the same value of the Weight of the Meatloaf, which is what we want.
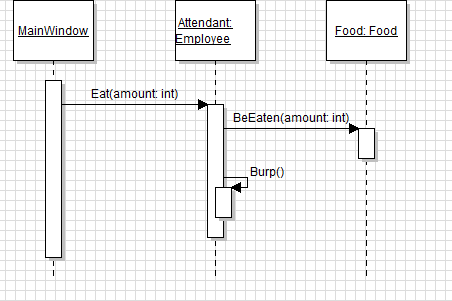
In sequence diagrams the parameter being passed is shown below. While there isn't a concrete way to tell that the amount parameter is the same in both places, keeping the name of the parameter the same throughout the application helps.
For instance, the parameter name for the BeEaten method can be anything.
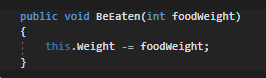
But doing may cause confusion for anyone reading the sequence diagram because the names will be different.