Let's take a look at the BeEaten method in the Food class.
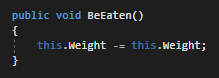
Currently when this method runs the food item's weight goes down once and only once and then is done. But we want the person eating to only eat while they're hungry or if there's actually food to eat.
The employee also gains all the Weight of the food when they Eat, but we don't want to make them have gut rot if they're eating a giant meal so we want them to only gain the Weight of the food that they eat.
To start, we've given the Employee a field of type int named HungerLevel that determines how hungry they are. Sam will have a HungerLevel of 4. We can pass the Employee into the BeEaten method to use the HungerLevel.
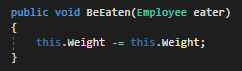
 Note: Passing 'this' into a method means 'passing the current instance of the class'. We will cover this more later, but for this example know that it passes the Sam object.
Note: Passing 'this' into a method means 'passing the current instance of the class'. We will cover this more later, but for this example know that it passes the Sam object.
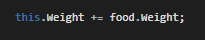
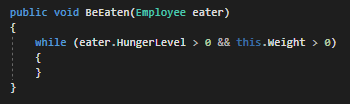
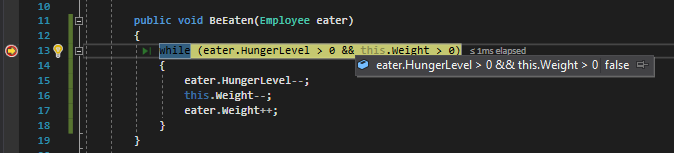
Now we can define a while loop that checks if the Employee's HungerLevel is greater than 0 and if the Weight of the Food is greater than 0. We only want to have this conditional evaluate false if either one of those logic checks evaluate to false (are 0).
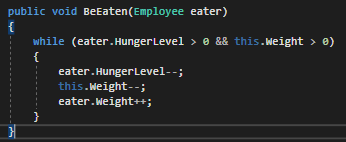
Every time the conditional runs we want the Employee's HungerLevel to go down, the Weight of the Food to go down, and the Weight of the Employee to go up.
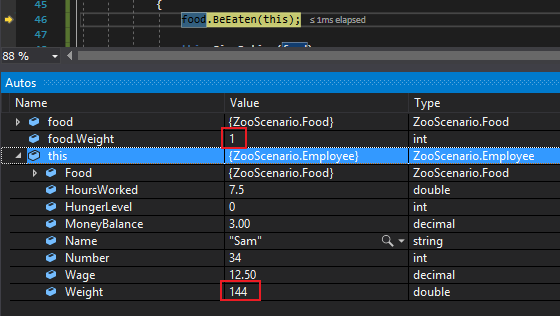
So when we run this we can see that the the Employee's (Sam) HungerLevel is 4 and the Weight of the Food is 5. Because both of these values are greater than 0 the conditional will evaluate to true and the code inside the while loop will run.
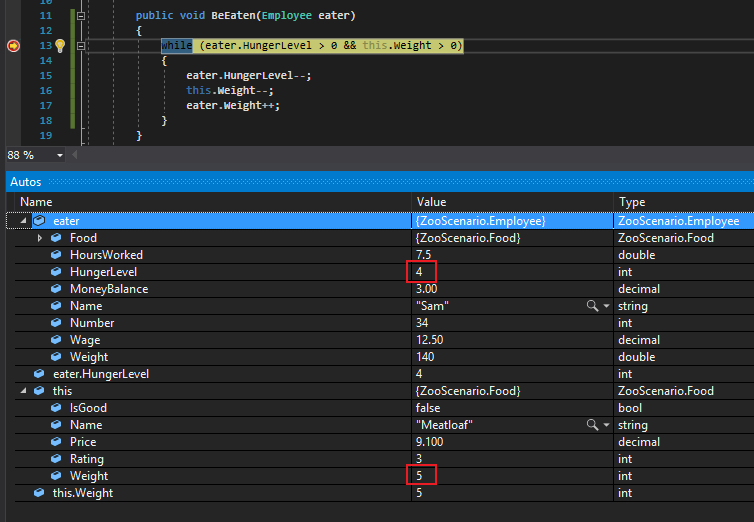
By the end of the first pass, Sam's HungerLevel is 3 instead of 4, the Meatloaf is 4lbs instead of 5lbs and Sam's Weight is 141 instead of 140.
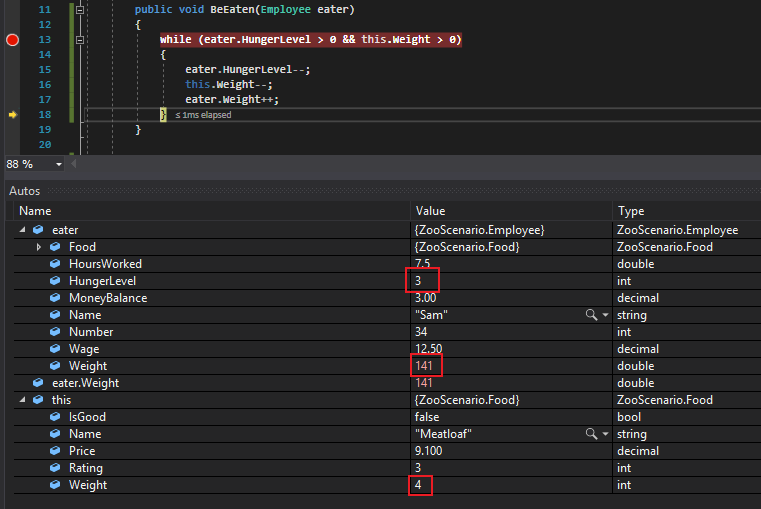
If we continue, the debugger will go back to the conditional to check it again. If it's still true, the code inside the while loop will run again. Since 3 and 4 are both greater than 0, the conditional will evaluate to true and the code will run.
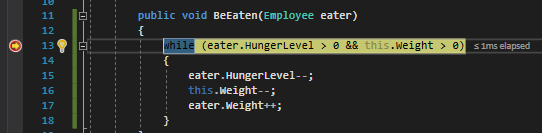
By the end of the second pass, Sam's HungerLevel is 2, the Meatloaf's Weight is 3 and Sam's Weight is 142.
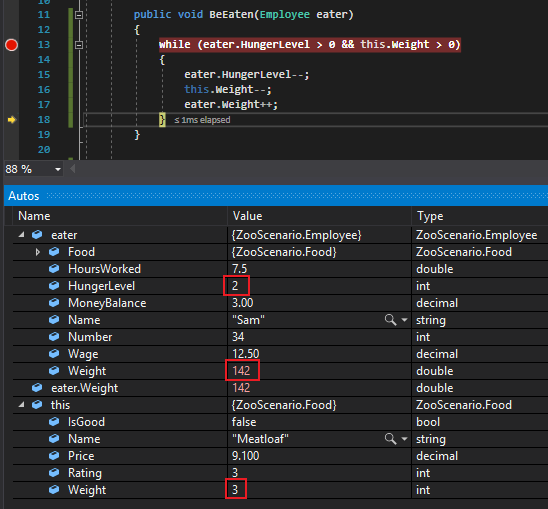
By the end of the fourth pass, Sam's HungerLevel is 0, the MeatLoaf's Weight is 1 and Sam's Weight is 144.
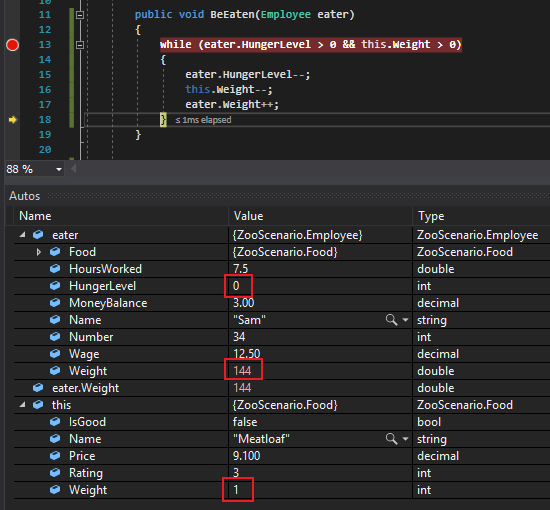
So now the conditional will evaluate to false because the HungerLevel is not greater than 0 anymore.
The debugger will then break out of the while loop and go back to the call. Here we can see that there is 1lb of Meatloaf left and Sam has gain 4lbs instead of the 5 that the Meatloaf weighed.