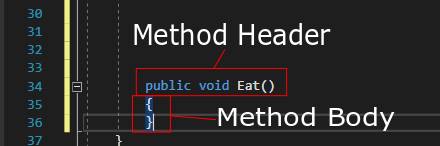
The two parts of a method are the method header and method body.
In the method header, there are several parts including visibility, return, name, and parameters.
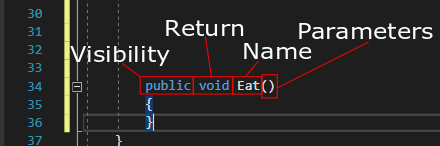
Visibility: Relates to what can access that particular method. The three visibility modifiers we will be using in this course are public, private and protected. Visibility can also be referred to as 'protection level'.
Return: The return portion of the method header defines what that method should be returning. Void means the method should not be returning anything. Any other type (either primitive or custom) can be used instead of void.
Name:This is the name of the method and can be named anything you would like granted it makes logical sense. In this course you will be given the names of the methods.
Parameters: Parameters are anything that the method "needs" in order to function properly. All methods must at least have empty parenthesis (no parameters) to define it correctly.
Method body: The method body contains the code that you would like the method to execute. An empty method body like the one above does nothing. All methods must have a pair of curly braces after the method header to define it correctly.
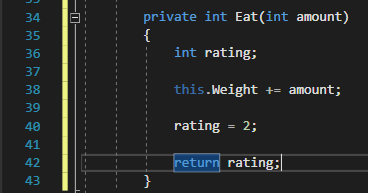
In the example below, the visibility is private, the return type is int, the name is Eat and the parameter is an amount of type int. The code inside the curly braces {} is the method body.