&& is the equivalent of an AND statement. When used in a logic check, both sides of the conditional need to evaluate to true for the entire logic check to evaluate to true.
if (true && true) the entire conditional will be true.
if (true && false) the entire conditional will be false.
if (false && true) the entire conditional will be false.
if (false && false) the entire conditional will be false.
For example, we may have a conditional that checks for a range...
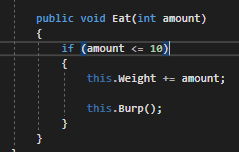
...but what if the amount parameter is a negative number? That wouldn't make sense and we can check that with multiple conditions. By adding an && with an additional check to make sure the amount is greater than 0...
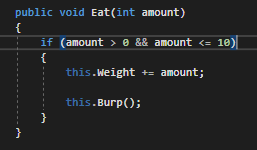
...you can ensure only numbers within that range are acceptable. Because 5 is within the range, the entire conditional will evaluate to true.
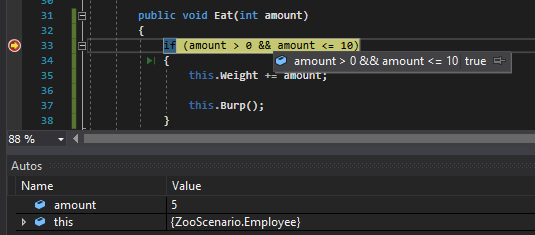
If I change the weight of the food to negative, however...
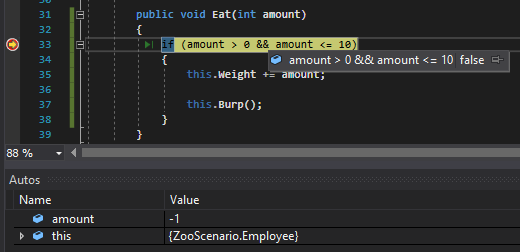
The conditional will evaluate to false because -1 is not greater than 0.
|| is the equivalent of an OR statement. When used in a logic check, if at least one of the conditionals is true the entire conditional will evaluate to true.
if (true || true) the entire conditional will be true.
if (true || false) the entire conditional will be true.
if (false || true) the entire conditional will be true.
if (false || false) the entire conditional will be false.
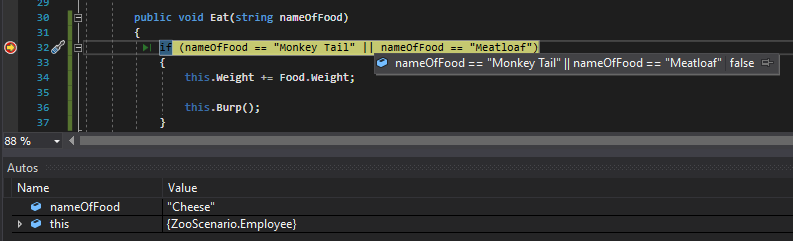
Let's say Sam is really picky and only wants to eat a Monkey Tail or Meatloaf. We will change the parameter of the Eat method to a type of string named 'nameOfFood' and pass in the Name of the Food item.
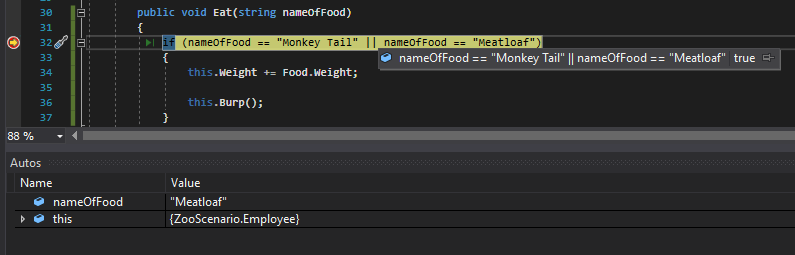
Then, we want to check if the name of the food passed in is either Monkey Tail or Meatloaf.

When we run the application and check the conditional it will evaluate to true because the nameOfFood parameter is the same as 'Meatloaf' in at least one of the conditionals.
Let's change the name of the Food item to something else...
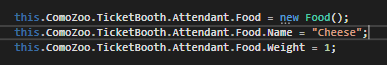
Now the entire conditional will evaluate to false because neither of the conditionals is true.