 Introduction To Programming
Introduction To Programming 10-152-310
Learning Plan 3 : Math and Operators
Simple Assignment Operator
Making variables and putting data into them.
What does data look like?
Numbers:
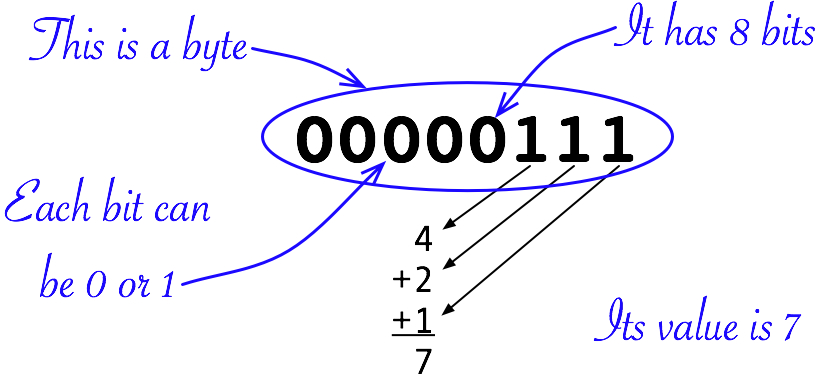
- Here's what the number 7 looks like in the computer:
00000000000000000000000000000111
- That's 32 bits in a row, which is maybe a little overwhelming. So, we break up the bits into groups of 8 that we call bytes. (You've probably heard that term, like in a 250GB hard drive. That's 250 billion bytes!)
00000000 00000000 00000000 00000111
- For the sake of discussion, we'll not worry about the first 3 bytes since they are all zeros. We'll just look at the last byte.
00000111
- Now we'll blow it up and look at what it means. The computer only understands base 2 arithmetic. The rightmost bit is the ones position, the next one to the left is the twos positions, next is the fours, etc.
Inspect with Firefox Menu - Here's what 10 looks like:
00001010
- Here's 255:
11111111
- And here's 682 but we had to add back the next byte:
00000010 10101010
Characters
- What about letters? Here's what the letter A is in the computer:
01000001
- Huh? That looks like a number! Yep, that's what everything is in the computer. That's also the number 65.
- How does the computer know that it's an A and not 65?
- Because we tell it that it's an A. That's what Assignment means.
Assignment
Assignment is setting a variable to a value and telling the computer the value's type.
- In JavaScript we do this by simply assigning a value to a variable. JavaScript figures out what type based on how you write the value:
- Numbers: 45, 123.99
- Strings: "this is a string", "Here's another", "12.99"
- A number is declared by not using quotes.
- A string is declared with the quotes, even if the value is a number.
- There are several ways to do assignment in JavaScript. The simplest is the Simple Assignment Operator.
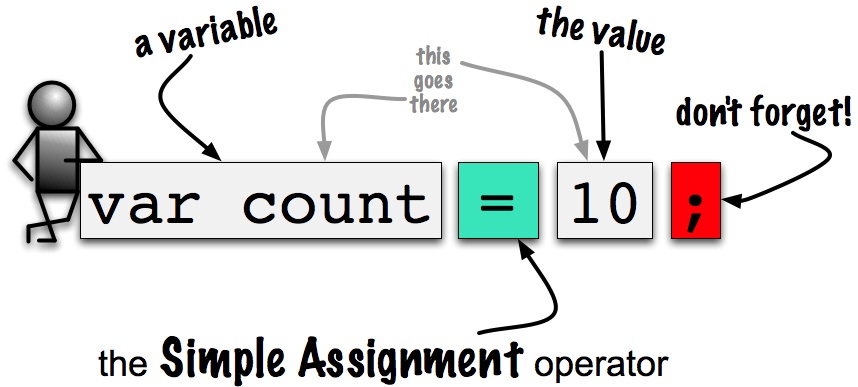
Simple Assignment - Simple Assignment when declaring the variable:
- Simple Assignment after the variable has been declared. This can happen anywhere in your code after the declaration.
- Simple Assignment with Math
- Simple Assignment by replacing the value of a variable:
- Simple Assignment to a new type. JavaScript is what is sometimes called a "loosely typed" language. This means that variables can be any type and you can change their type. Many other languages, like Java and C#, are "strongly typed" languages. Their variables have to be declared a type and you can't change the type.
- You can also assign the value of a variable with the results of a function. This is very common and will look very normal quickly.
- Simple Assignment can be done to a variable "in-place", from itself to itself.